High Fuel Consumption: 14 most common causes

Fuel consumption is one of the most important factors when buying a car, especially for people who use their car daily and achieve high mileage each month.
And even if that's not the case, fuel consumption is the thing that interests almost every owner of the car. So what's the cause of high fuel consumption? Let's check out the 14 most common causes of it.
Content
- Introduction
- 1. Inappropriate driving style
- 2. Air resistance
- 3. Underinflated tires
- 4. Clogged air filter
- 5. Constant-velocity joint and bearings
- 6. Hanging brake caliper
- 7. Mass flow sensor failure
- 8. Lambda probe malfunction
- 9. Spark plugs
- 10. The engine
- 11. Clogged particulate filter
- 12. Engine control unit and sensors
- 13. Fuel system
- 14. Air conditioning compressor
- Conclusion
Introduction
First, fuel consumption is not constant and is affected by several factors. These can vary from malfunctions, specific driving styles, weather conditions, car age, engine, etc.
However, the fuel consumption may be far away from the values written in the tech specs given by the car manufacturer. That may be the case even if the engine is in good condition and your driving style can be described as economical.
If you notice a significant increase in fuel consumption, it will almost certainly mean one of the problems mentioned below. So let's look at the most common malfunctions and problems behind increased fuel consumption.
1. Inappropriate driving style
Among the most common problems that can cause high fuel consumption we can include an inadequate or inappropriate driving style. This is a more common problem with manual transmissions since it allows you to choose the wrong gear, causing an increase in fuel consumption.
Likewise, quickly accelerating and decelerating before every crossroad is not an excellent way to save fuel. However, if you are sure that your driving style has not changed, but fuel consumption has increased, the problem might be something else.
2. Air resistance
Fuel consumption is significantly affected by aerodynamic resistance, which is increased considerably by transporting luggage, bicycles, skis, or other unnecessary items on top of the roof.
The increased aerodynamic resistance is also due to open windows or a sunroof. Another factor affecting aerodynamic resistance and, thus also, fuel consumption is loose undercarriage or the lower engine cover.
3. Underinflated tires

Improper tire pressure significantly affects fuel consumption. Suppose the tire pressure is lower, rolling resistance increases and thus fuel consumption. That is why it is essential to check the tire pressure regularly and, if necessary, inflate the tires to the prescribed pressure.

Incorrect tire pressure not only increases fuel consumption but also worsens the car's driving characteristics and, last but not least, also contributes to faster tire wear.
4. Clogged air filter

The air filter has a significant effect on the operation of the engine. For this reason, you should not forget about its regular replacement. If the air filter is excessively clogged, it will cause insufficient air to enter the cylinders. This problem can be eliminated very quickly and relatively cheaply.

Air filter: What does it do, and what are its types?
A clogged air filter is manifested by a noticeable decrease in performance and increased fuel consumption. So, if you notice that your car's engine is not as powerful as it used to be and the fuel consumption has increased, you should first focus on checking and, if necessary, replacing the air filter.
5. Constant-velocity joint and bearings

Increased consumption due to increased resistance can also be caused by a damaged or worn constant-velocity joint or bad bearings. If any of these components are worn or damaged due to increased resistance, there may be a loss of engine energy transmitted to the wheels of the car, leading to increased fuel consumption.

Constant-Velocity Joint: Why is it important?
Signs of a bad CV joint include clicking or popping noises when turning, vibrations while driving at high speeds, and grease leaking from the joint. You can quite easily recognize these issues just by hearing them. If the wheel bearings are on the verge of their lifespan, they are signaled by increased noise while driving.
6. Hanging brake caliper

Another problem with increased fuel consumption can be a hanging or stuck brake caliper. If that happens, the brake pad would always be in contact with the brake rotor, even if slightly.
You might not be aware of this issue, depending on how much the brake caliper is stuck, but if you do, it would feel like you're driving a car with the brakes lightly applied all the time.
7. Mass flow sensor failure

Mass flow sensor malfunction might be another cause behind increased fuel consumption. It can occur if the mass flow sensor is excessively polluted or damaged. It may still continue to function, but the changes in engine operation are significant and can be noticed even by a complete layman.

The most common symptoms of mass flow sensor failure include difficult engine starts, high or low engine idle speed, uneven engine running, jerking during acceleration, or engine stalling. This problem can be easily eliminated by replacing the component.
8. Lambda probe malfunction

Lambda probe is a frequent culprit of increased fuel consumption in petrol engines. A lambda probe is a sensor in the exhaust pipe that compares the air in the exhaust pipe with the air around the engine and creates an electrical signal based on a chemical reaction.

Lambda probe: What does this device do?
This signal is sent to the engine control unit, which then uses the throttle valve and injectors to adjust the ratio of fuel and air. Simply put, the vehicle uses the lambda probe to make the engine work economically.
In some cases, it is possible to physically identify the lambda probe's malfunction because it is clogged with a large amount of soot. However, a lambda probe malfunction is not always detected by its physical inspection, so the best solution is to go straight to the repair shop, connect the car for diagnostics, and replace it if it's damaged.
9. Spark plugs
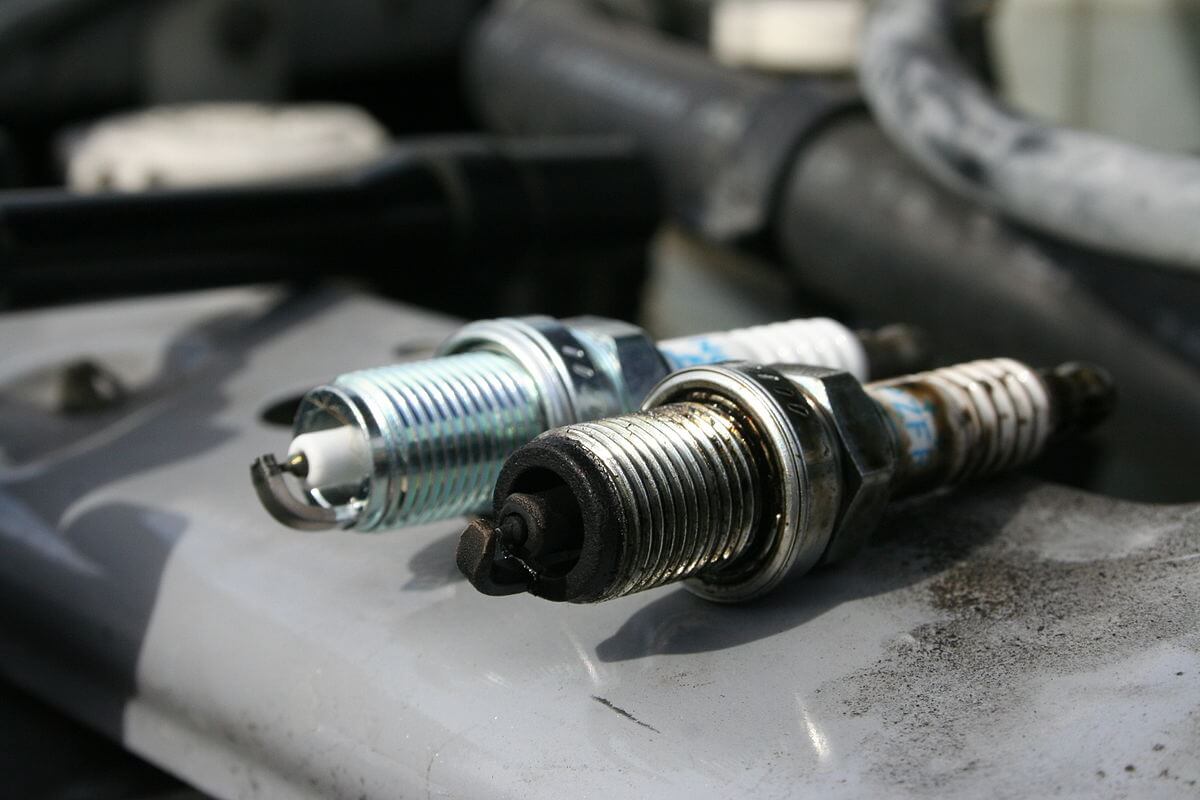

If the spark plugs are excessively worn, the combustion of the fuel mixture is not optimal. This leads to increased fuel consumption and reduced performance. Replacing spark plugs is straightforward and inexpensive, so no one should neglect it.
10. The engine

Damage to the engine itself sounds like an obvious cause of increased fuel consumption, but which components cause this issue? Worn cylinders, cracked cylinder heads, head gaskets, worn piston rings, or damaged valves cause combustion chamber leaks, resulting in lower compression pressures.
The compression pressure of the cylinders is measured using a compression gauge. Before measuring the compression pressure, the engine is warmed to operating temperature to define the clearances between the piston and the cylinder. The compression gauge is screwed into the cylinder head instead of the spark plug.
Subsequently, the engine is revved using the starter while the throttle valve is fully open - the accelerator pedal is fully pressed. The compression pressure is shown on the needle of the compression meter, which records the highest pressure reached. The compression pressure must be the same in all cylinders.
11. Clogged particulate filter

A clogged particulate filter can also be to blame for increased fuel consumption. A diesel particulate filter is a device that removes carcinogenic and fine dust particles from the exhaust gases of cars with a diesel engine.

The filter captures solid particles, which it eventually burns to clean itself. However, this problematic component likes to get dirty, especially if you only use your diesel car for short drives.
A clogged particulate filter is manifested by a significant reduction in performance but also by an increase in fuel consumption. Unfortunately, replacing or cleaning this filter is not one of the cheapest things.
12. Engine control unit and sensors

Another of the countless causes of increased fuel consumption may be the engine control unit or various sensors that send data to it. The most important sensors include the lambda probe, mass flow sensor, crankshaft position sensor, knock sensor, coolant temperature sensor, or camshaft sensor.

Engine Control Unit: What is its function?
All these sensors send different information to the engine control unit. The engine control unit uses this data in order to operate the engine efficiently. These sensors, combined with the engine control unit, control the fuel injection timing, the fuel injection length, the ignition advance of the mixture, and many other things.
Suppose one of the sensors does not work properly. In that case, the engine control unit receives incorrect data, which can cause the incorrect amount of fuel to be injected into the cylinders or the incorrect timing of the ignition advance of the mixture.
However, the engine does not work properly in both cases, resulting in increased fuel consumption and lower performance.
13. Fuel system
Problems with leaking fuel system pipes are especially evident in older cars. The rubber hoses of the fuel system become brittle (crack) over time, which leads to fuel leakage. You can detect this problem very easily because it is manifested by the smell of fuel in the interior of the car and its vicinity.
You can also notice a fuel leak by checking whether any fuel stains are on the ground where you park. Another symptom of a fuel system leak is that it is more difficult to start precisely because air is getting into the fuel system.
14. Air conditioning compressor
A magnetic clutch controls the air conditioning compressor. This clutch can become damaged and leave the compressor running continuously. Air conditioning can increase fuel consumption from a small to a large amount, depending on the type of engine.
A permanently switched-on air conditioning compressor can thus cause a significant increase in fuel consumption without you even noticing that something is wrong with the car.
Conclusion
Some countless other problems and malfunctions can cause increased fuel consumption. However, this article focused on the most common problems that may bother you.
If it seems your car is asking for more than it should, use this as a baseline of malfunctions that may cause an excessive appetite for your car. At the same time, we wish that the solution to your problem is as simple and cheap as possible.
